2023年10月8日,医学图像计算与计算机辅助介入领域的国际顶级会议MICCAI(Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention)在加拿大温哥华拉开帷幕。医疗机器人研究院郑国焱教授、顾运副教授等团队共7篇论文被录取。
论文一
CT-guided, Unsupervised Super-resolution Reconstruction of Single 3D Magnetic Resonance Image
CT引导的无监督的3D MRI超分辨率重建
Jiale Wang, Guoyan Zheng
王佳乐(博士二年级),郑国焱
Deep learning-based algorithms for single MR image (MRI) super-resolution have shown great potential in enhancing the resolution of low-quality images. However, many of these methods rely on supervised training with paired low resolution (LR) and high-resolution (HR) MR images, which can be difficult to obtain in clinical settings. This is because acquiring HR MR images in clinical settings requires a significant amount of time. In contrast, HR CT images are acquired in clinical routine. In this paper, we propose a CT-guided, unsupervised MRI super-resolution reconstruction method based on joint cross-modality image translation and super-resolution reconstruction, eliminating the requirement of high-resolution MRI for training. The proposed approach is validated on two datasets respectively acquired from two different clinical centers. Experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed approach over the state-of-the-art methods.
基于深度学习的MRI超分辨率算法在提高低质量图像的分辨率方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,这些方法中大部分都依赖于配对的低分辨率和高分辨率MR图像进行有监督的训练,配对的图像在临床中很难获得。这是因为在临床中获取高分辨率的MR图像需要大量的时间。相比之下,高分辨率的CT图像在临床中较容易获得。本文提出了一种基于联合跨模态图像转换和超分辨率重建的CT引导的无监督的MRI超分辨率重建方法,不需要高分辨率的MRI就可以完成训练。该方法在两个不同的临床中心分别获得的两个数据集上进行了验证。实验结果表明,该方法的性能优于现有最好的方法。

论文二
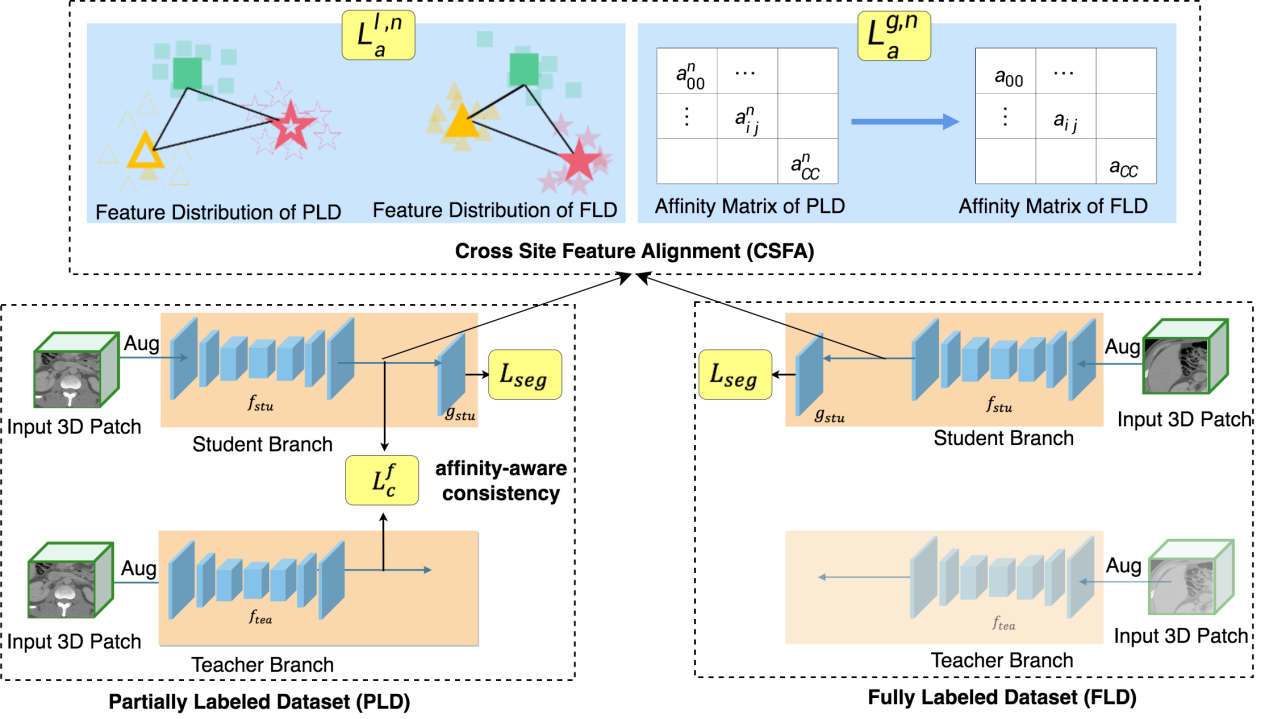
Partially Supervised Multi-Organ Segmentation via Affinity-aware Consistency Learning and Cross Site Feature Alignment
基于相似度感知一致性学习和跨中心特征对齐的部分监督多器官分割算法
Qin Zhou, Peng Liu, Guoyan Zheng
周芹(博士后),刘鹏(博士四年级),郑国焱
Partially supervised segmentation (PSS) has attracted increasing attention in multi-organ segmentation (MOS). However, facing with challenges from lacking sufficiently labeled data and cross-site data discrepancy, PSS remains largely an unsolved problem. In this paper, to fully take advantage of the unlabeled data, we propose to model voxel-to-organ affinity in embedding space into consistency learning, ensuring consistency in both label space and latent feature space. Furthermore, to mitigate the cross-site data discrepancy, we propose to propagate the inter-organ affinity relationships across different sites, calibrating the multi-site feature distribution from a statistical perspective. Extensive experiments manifest that our method generates favorable results compared with other state-of-the-art methods, especially on hard organs with relatively smaller sizes.
部分监督分割在多器官分割任务中获得了越来越多的关注。然而, 由于缺乏足够的标注样本以及不同中心的数据差异,部分监督分割在很大程度上仍然是一个未解决的问题。本文中,我们提出将体素-器官在特征空间的相似度关系引入一致性学习框架,通过确保标签空间和特征空间的一致性来充分利用无标签数据。此外,为了减轻跨中心数据差异的影响,我们提出在不同中心之间传播跨器官的相似度关系,以此来从统计层面实现多中心数据的特征分布对齐。大量实验表明,与其他算法相比,我们的算法取得了更好的性能,尤其在尺寸相对较小的较难分割器官上表现更佳。
论文三
FedContrast-GPA: Heterogeneous Federated Optimization via Local Contrastive Learning and Global Process-aware Aggregation
FedContrast-GPA: 基于局部对比学习和全局过程感知聚合的异质联邦优化
Qin Zhou, Guoyan Zheng
周芹(博士后已出站),郑国焱
Recently, federated learning has emerged as a promising strategy for performing privacy-preserving, distributed learning for medical image segmentation. However, the data heterogeneity as well as system heterogeneity makes it challenging to optimize. Existing methods try to tackle the heterogeneity issues in federated networks via proximal restriction or re-parameterization on local models, which may limit the convergence potential of local models. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end FedContrast-GPA framework to jointly address the data-level and system-level heterogeneity. In specific, for data heterogeneity, we aim to enhance the feature representations in local model training via an intra-client and inter-client local prototype based contrastive learning scheme. As for system heterogeneity, we further propose a simple process-aware aggregation scheme to achieve effective straggler mitigation. Experimental results on six prostate segmentation datasets demonstrate large performance boost over existing state-of-the-art federated optimization methods.
近年来,联邦学习在针对隐私保护的分布式医疗图像分割领域成为炙手可热的研究领域。然而,数据异质以及系统异质问题使得联邦学习的优化问题十分困难。现有算法尝试通过相近约束或者重参数等方法来解决联邦学习中的异质问题,这会限制局部模型的收敛。本文中,我们提出了一种端到端的框架来同时解决数据异质和系统异质问题。具体来说,针对数据异质,我们提出基于中心内部和跨中心的局部原型特征的对比学习框架来增强本地模型更新过程中的特征表达。另一方面,针对系统异质问题,我们提出了一种简单但十分有效的进程感知模型融合算法,可以有效缓解系统异质导致的落后者问题。在六个前列腺分割数据集上的结果表明我们的算法与其他先进的算法相比,可以实现较大的性能提升。

论文四
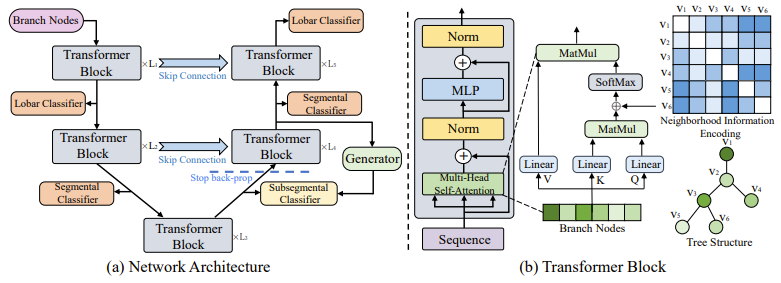
AirwayFormer: Structure-Aware Boundary-Adaptive Transformers for Airway Anatomical Labeling
用于气道解剖标记的结构感知边界自适应分割算法
Weihao Yu , Hao Zheng, Yun Gu, Fangfang Xie , Jiayuan Sun , Jie Yang
喻伟豪,郑昊,顾运,谢芳芳,孙加源,杨杰
Pulmonary airway labeling identifies anatomical names for branches in bronchial trees. These fine-grained labels are critical for disease diagnosis and intra-operative navigation. Recently, various methods have been proposed for this task. However, accurate labeling of each bronchus is challenging due to the fine-grained categories and interindividual variations. On the one hand, training a network with limited data to recognize multitudinous classes sets an obstacle to the design of algorithms. We propose to maximize the use of latent relationships by a transformer-based network. Neighborhood information is properly integrated to capture the priors in the tree structure, while a U-shape layout is introduced to exploit the correspondence between different nomenclature levels. On the other hand, individual variations cause the distribution overlapping of adjacent classes in feature space. To resolve the confusion between sibling categories, we present a novel generator that predicts the weight matrix of the classifier to produce dynamic decision boundaries between subsegmental classes. Extensive experiments performed on publicly available datasets demonstrate that our method can perform better than state-of-the-art methods.
肺气道标记识别了支气管树中分支的解剖命名。这些细粒度的标签对于疾病诊断和术中导航至关重要。最近,已经提出了各种方法来完成这个任务。然而,由于细粒度的分类和个体间的变异,准确地标记每个支气管是具有挑战性的。一方面,用有限的数据训练网络以识别众多类别对算法设计构成了障碍。我们提议通过基于Transformer的网络来最大限度地利用潜在关系。合理地整合了邻域信息以捕捉树结构中的先验知识,同时引入了U形布局以利用不同命名级别之间的对应关系。另一方面,个体间的变异导致特征空间中相邻类别的分布重叠。为了解决兄弟类别之间的混淆问题,我们提出了一种新颖的生成器,用于预测分类器的权重矩阵,以产生子段类别之间的动态决策边界。在公开可用的数据集上进行的大量实验表明,我们的方法可以比现有的方法表现更好。
论文五
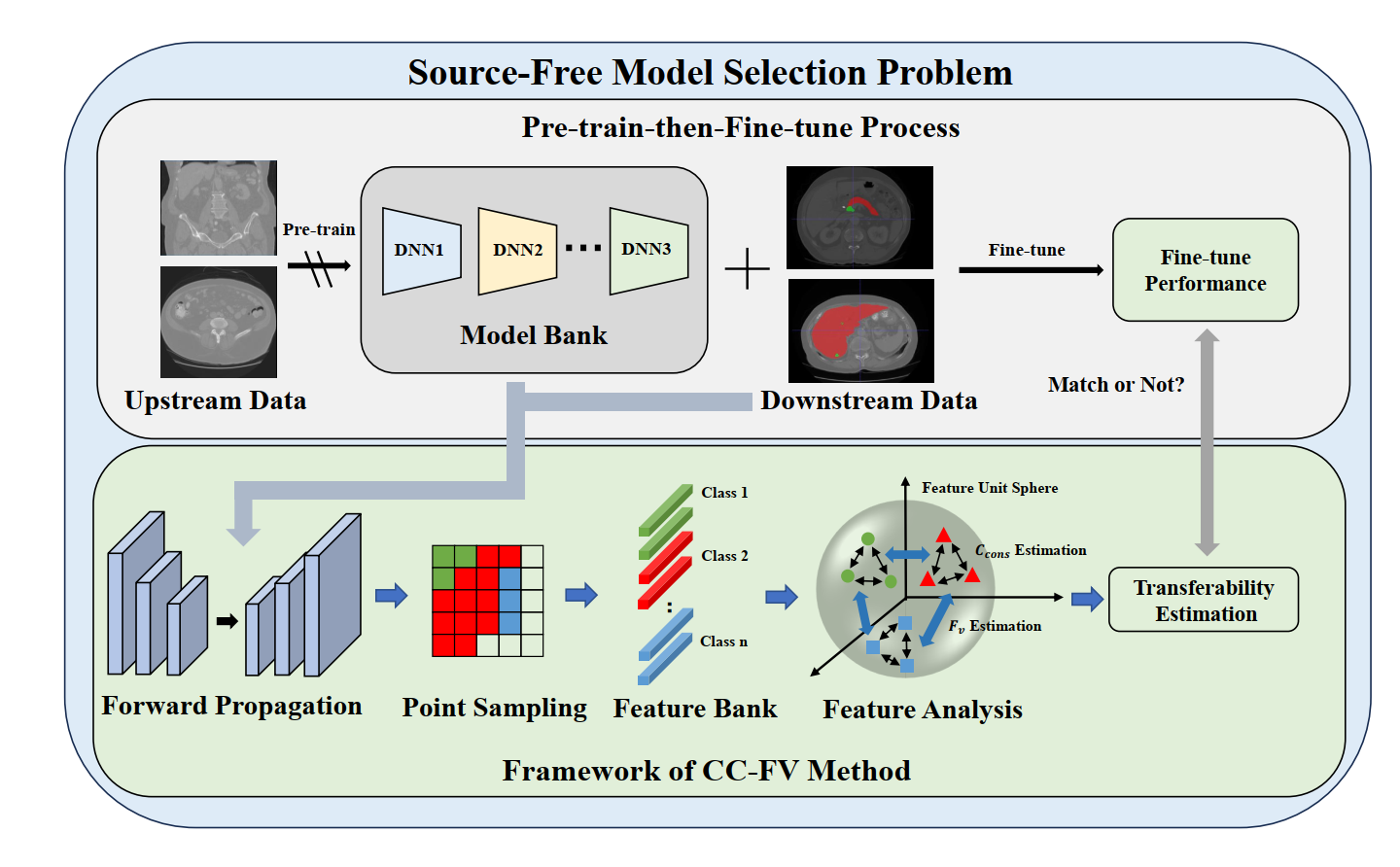
Pick the Best Pre-trained Model: Towards Transferability Estimation for Medical Image Segmentation.
挑选最佳预训练模型: 医疗图像分割的可迁移性评估
Yuncheng Yang, Meng Wei, Junjun He, Jie Yang, Jin Ye, Yun Gu
杨运成(研究生二年级),魏萌,何军军,杨杰,叶锦,顾运
Transfer learning is a critical technique in training deep neural networks for the challenging medical image segmentation task that requires enormous resources. With the abundance of medical image data, many research institutions release models trained on various datasets that can form a huge pool of candidate source models to choose from. Hence, it’s vital to estimate the source models’ transferability (i.e., the ability to generalize across different downstream tasks) for proper and efficient model reuse. To make up for its deficiency when applying transfer learning to medical image segmentation, in this paper, we therefore propose a new Transferability Estimation (TE) method. We first analyze the drawbacks of using the existing TE algorithms for medical image segmentation and then design a source-free TE framework that considers both class consistency and feature variety for better estimation. Extensive experiments show that our method surpasses all current algorithms for transferability estimation in medical image segmentation.
迁移学习是训练深度神经网络的一项关键技术,用于需要大量资源的高难度医学图像分割任务。随着医学影像数据的丰富,许多研究机构都发布了在各种数据集上训练的模型,这些数据集可形成一个巨大的候选源模型池供用户选择。因此,估算源模型的可迁移性(即在不同下游任务中的泛化能力)对于正确、高效地重用模型至关重要。为了弥补将迁移学习应用于医学图像分割时的不足,我们在本文中提出了一种新的迁移性估计方法。我们首先分析了在医学图像分割中使用现有迁移学习算法的缺点,然后设计了一个无源迁移学习框架,该框架同时考虑了类的一致性和特征的多样性,以实现更好的估计。广泛的实验表明,我们的方法超越了目前所有用于医学图像分割的可迁移性估计算法。
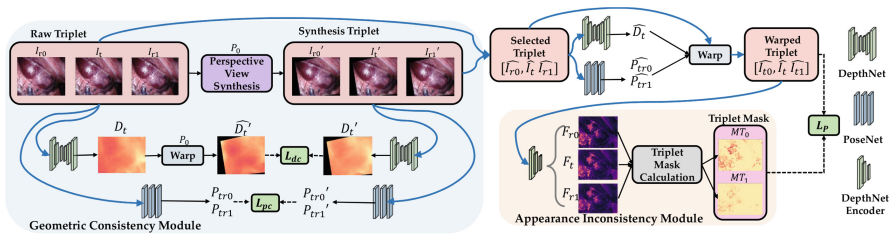
论文六
Triplet Consistent Learning for Odometry Estimation of Monocular Endoscope
基于三元组一致性学习的单目内窥镜里程计估计算法
Hao Yue,Yun Gu
岳浩(硕士二年级),顾运
The depth and pose estimations from monocular images are essential for computer-aided navigation. Since the ground truth of depth and pose are difficult to obtain, the unsupervised training method has a broad prospect in endoscopic scenes. However, endoscopic datasets lack sufficient diversity of visual variations, and appearance inconsistency is also frequently observed in image triplets. In this paper, we propose a triplet-consistency-learning framework (TCL) consisting of two modules: Geometric Consistency module(GC) and Appearance Inconsistency module(AiC). To enrich the diversity of endoscopic datasets, the GC module generates synthesis triplets and enforces geometric consistency via specific losses. To reduce the appearance inconsistency in the image triplets, the AiC module introduces a triplet-masking strategy to act on photometric loss. TCL can be easily embedded into various unsupervised methods without adding extra model parameters. Experiments on public datasets demonstrate that TCL effectively improves the accuracy of unsupervised methods even with limited number of training samples.
单目图像的深度和位姿估计对于计算机辅助导航至关重要。由于深度和位姿的真实值难以获取,无监督训练方法在内窥镜场景中具有广阔的前景。然而,内窥镜数据集缺乏足够多的视觉变化多样性,并且经常存在图像三元组中的外观不一致性。在本文中,我们提出了一个三元组一致性学习框架(TCL),由两个模块组成:几何一致性模块(GC)和外观不一致性模块(AiC)。为了丰富内窥镜数据集的多样性,GC模块生成合成三元组,并通过特定损失函数强化几何一致性。为了减少图像三元组中的外观不一致性,AiC模块引入了三元组遮蔽策略,用于处理光度损失。TCL可以轻松嵌入各种无监督方法,而不需要额外的模型参数。在公开数据集上的实验证明,即使在训练样本数量有限的情况下,TCL有效地提高了无监督方法的准确性。
论文七
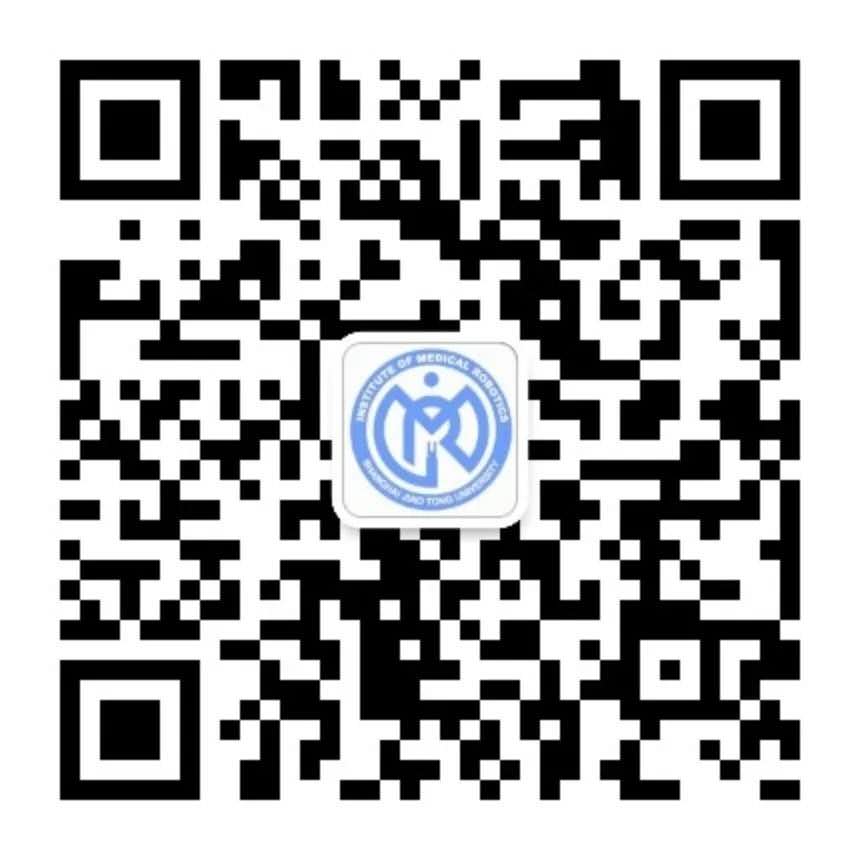
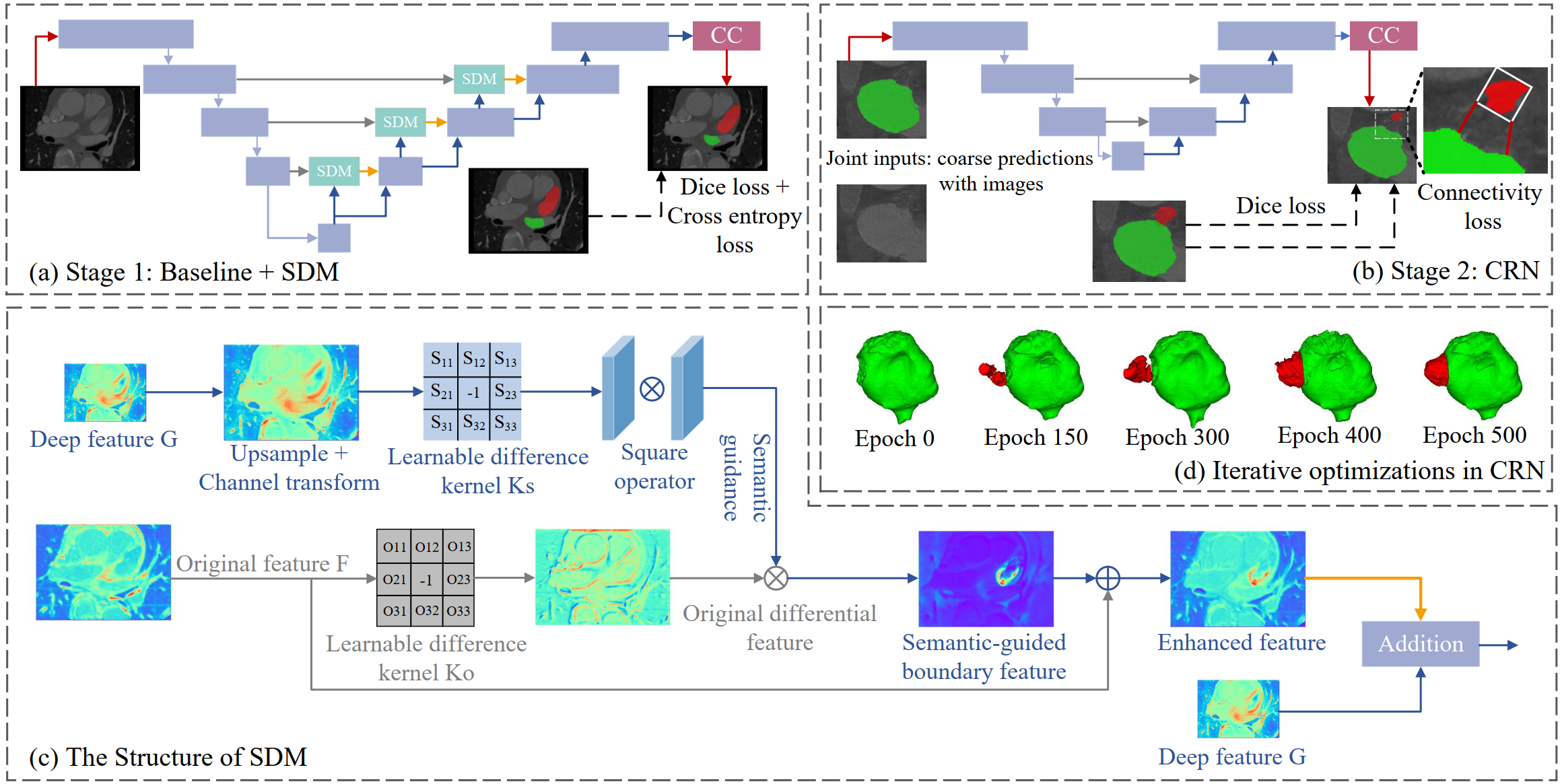
Semantic difference guidance for the uncertain boundary segmentation of CT left atrial appendage
基于语义差分引导的左心耳CT图像不确定边缘分割算法
Xin You, Ming Ding, Minghui Zhang, Yangqian Wu, Yi Yu, Yun Gu, and Jie Yang
游鑫(博士四年级),丁茗(新华医院医生),张明辉(博士四年级),吴扬谦(硕士三年级),郁怡(新华医院医生),顾运,杨杰
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most common types of cardiac arrhythmia, which is closely relevant to anatomical structures including the left atrium (LA) and the left atrial appendage (LAA). Thus, a thorough understanding of the LA and LAA is essential for the AF treatment. In this paper, we have modeled relative relations between the LA and LAA via deep segmentation networks for the first time, and introduce a new LA & LAA CT dataset. To deal with uncertain boundaries between the LA and LAA, we propose the semantic difference module (SDM) based on diffusion theory to refine features with enhanced boundary information. Besides, disconnections between the LA and LAA are frequently observed in the segmentation results due to uncertain boundaries of the LAA region and CT imaging noise. To address this issue, we devise another connectivity-refined network with the connectivity loss. The loss function exerts a distance regularization on coarse predictions from the first-stage network. Experiments demonstrate that our proposed model can achieve state-of-the-art segmentation performance compared with classic convolutional-neural-networks (CNNs) and recent Transformer-based models on this new dataset. Specifically, SDM can also outperform existing methods on refining uncertain boundaries. Codes are available at https://github.com/AlexYouXin/LA-LAA-segmentation.
房颤的产生与左心房和左心耳结构密切相关,被视作心律失常的最常见症状之一。为此,对于左心房和左心耳结构的全面研究有助于房颤患者的诊断和治疗。在本工作中,我们首次通过深度分割网络对左心房和左心耳的相对关系进行建模,并贡献了一个全新的左心房和左心耳数据。为解决左心房和左心耳间不确定边界的精准分割问题,我们基于扩散理论提出了语义差分模块用以精炼深度特征,使其具备更丰富的边缘信息。此外,由于CT的成像噪声,左心房与左心耳的预测结果中频繁出现不连通的区域。为解决这个问题,我们设计了带有连通性损失的连通优化网络作为第二阶段。该损失函数对第一阶段的粗分割结果施加了距离正则。实验结果表明我们所提出的模型优于经典的卷积神经网络以及Transformer网络,达到了最先进的分割性能。同时,语义差分模块也优于其他用于优化不确定边缘的方法。代码已开源至https://github.com/AlexYouXin/LA-LAA-segmentation.